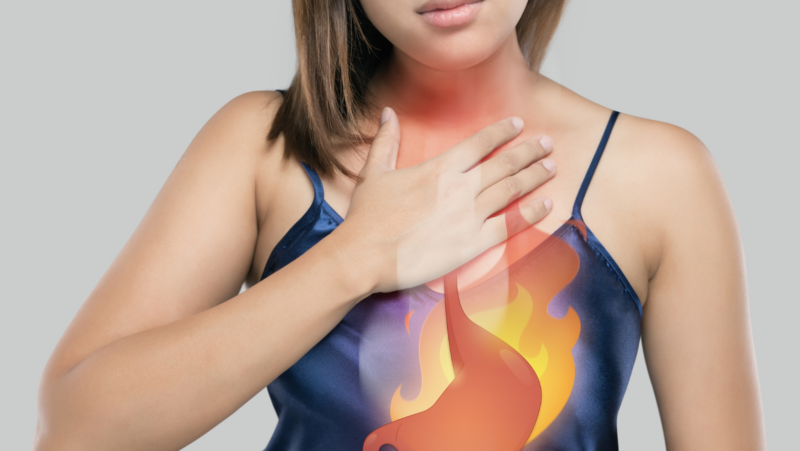
Chronic stress has long been recognized as a silent contributor to a range of health issues. Historically, stress was viewed as a temporary response to immediate threats, a natural part of human survival. However, modern research has shown that prolonged exposure to stress can lead to serious physical and mental health problems. From heart disease to anxiety disorders, chronic stress affects multiple aspects of well-being. With today’s fast-paced, demanding lifestyles, stress has become more persistent, impacting people across all walks of life. Understanding the link between stress and health conditions is key to preventing long-term damage and promoting healthier lives.
Observation:
Imagine stress as a slow leak in a tire. Initially, it may not seem like a big deal, but over time, it can lead to major problems. Just like a tire needs air to function, our bodies need balance. When stress is not managed, it affects our health in ways that may not be obvious at first but can eventually cause significant harm.
What is Chronic Stress?
Chronic stress is the constant feeling of pressure or tension over a prolonged period. Unlike short-term stress, which is a normal response to daily challenges, chronic stress lingers for weeks, months, or even years. This kind of stress can result from ongoing issues, such as work pressure, relationship difficulties, or financial struggles. Over time, the body remains in a heightened state of alert, releasing stress hormones like cortisol. While this response is helpful in short bursts, prolonged exposure can be harmful. Chronic stress can lead to mental and physical exhaustion, and if not addressed, it can trigger various health conditions like high blood pressure, depression, and digestive problems. Recognizing chronic stress early is important because, unlike acute stress, it can have lasting impacts that affect not only the body but also a person’s emotional well-being and quality of life.
Impact on Physical Health
Chronic stress can take a serious toll on physical health, affecting the body in multiple ways. One of the most common impacts is on the cardiovascular system. When stress is prolonged, the body releases stress hormones that cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. Over time, this can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other serious health conditions. Stress also weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Additionally, the digestive system can suffer as chronic stress may lead to issues like ulcers, acid reflux, and irritable bowel syndrome.
These physical problems can worsen if stress leads to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as excessive alcohol consumption. Many individuals turn to alcohol as a way to unwind, but this can exacerbate the effects of stress, leading to a vicious cycle. In some cases, individuals may need professional help, such as enrolling in an alcohol rehab program, to break free from the harmful effects of stress and alcohol dependency. By addressing the root cause of stress and seeking proper treatment, it is possible to reduce the physical health risks associated with chronic stress.
Facts:
Studies show that individuals who experience chronic stress are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, hypertension, and other stress-related conditions. Managing stress through therapy, exercise, and relaxation techniques can significantly reduce these risks.
Effects on Mental Health
Chronic stress not only harms the body but also significantly impacts mental health. It can lead to anxiety, depression, and other emotional difficulties. Prolonged stress may affect the brain’s ability to regulate emotions, making individuals feel overwhelmed and helpless. Stress also interferes with sleep patterns, which can further contribute to mental health challenges.
Here are some ways chronic stress impacts mental well-being:
- Increased anxiety leads to constant worry and fear.
- Depression causes feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and fatigue.
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions due to mental exhaustion.
The mental toll of chronic stress can be just as damaging as the physical effects, making it essential to address both aspects for overall well-being. Seeking support, therapy, and practicing relaxation techniques can help alleviate these mental health struggles.
Common Health Conditions Linked
Chronic stress is closely linked to a range of serious health conditions, both physical and mental. Over time, the constant release of stress hormones can cause lasting damage to the body. One of the most common physical conditions related to chronic stress is cardiovascular disease. High blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke are more prevalent in individuals who experience prolonged stress. Chronic stress also increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as it can affect how the body processes glucose. Additionally, stress is a major contributor to mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. The constant feeling of being overwhelmed and anxious can lead to a decrease in mood and cognitive function, affecting everyday life. Stress is also linked to digestive problems like irritable bowel syndrome and acid reflux, as the digestive system becomes more sensitive under stress. Chronic stress can also worsen pre-existing conditions such as asthma or autoimmune diseases, further complicating health management.
Research:
According to a study by the American Psychological Association, nearly 75% of Americans report experiencing moderate to high levels of stress. The research also shows that those with chronic stress are twice as likely to develop serious health conditions, underlining the importance of managing stress early to prevent these issues from escalating.
Managing Chronic Stress Effectively
There are various strategies for managing chronic stress, each offering its own set of advantages and challenges. Traditional methods of therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), are highly effective in helping individuals understand and change their stress responses. However, therapy can be time-consuming and expensive, and not everyone may have access to it.

On the other hand, self-care practices like meditation, exercise, and proper sleep hygiene can also help manage stress. These methods are more accessible and less costly but may take longer to show results and require consistent effort. Another approach is medication, which can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression caused by chronic stress. While medication offers quick relief, it doesn’t address the root cause of the stress and may come with side effects.
Case study:
A workplace implemented a stress management program that combined therapy, physical exercise, and meditation. Employees who participated showed a 40% reduction in reported stress levels over three months compared to those who used traditional methods alone. This program highlighted the importance of a multi-faceted approach, combining different strategies to help individuals manage stress effectively in both personal and professional settings.
A Path to Wellness
Understanding the connection between chronic stress and health conditions is key to improving overall well-being. By recognizing the signs of stress and taking proactive steps, individuals can reduce their risk of developing serious health problems. Managing stress through therapy, lifestyle changes, and self-care practices helps maintain both physical and mental health. The more we focus on stress management, the better our chances of leading a balanced, healthier life. Taking small, consistent actions today can lead to long-term improvements in wellness and prevent future health complications.