Diabetes comes with unique challenges, especially when managing our blood glucose levels. Whether you are newly diagnosed or have lived with the condition for some time, navigating blood sugar management can be overwhelming and frustrating. Many people struggle to maintain a healthy lifestyle despite their best efforts.
This article will explore the fundamentals of control, from identifying which foods are best suited for keeping your sugar in check to understanding when medication may be needed – all while creating a balanced lifestyle that works for you. We’ll provide valuable tips that everyone living with diabetes can use and resources to build more knowledge about your individual needs and health goals. With these tools, we will work towards sustainable solutions for your glycemic health journey one step at a time.
Introducing Diabetes and Blood Sugar Management
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the bloodstream due to either insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of the hormone by the body. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe complications such as nerve damage, blindness, and kidney failure.
Achieving optimal blood sugar control involves making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, self-monitoring, and taking medication as a healthcare professional prescribes. Proper management of diabetes can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the risk of long-term health problems. Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the bloodstream due to either insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of the hormone by the body.
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe complications such as nerve damage, blindness, and kidney failure. Achieving optimal blood sugar control involves making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, self-monitoring, and taking medication as a healthcare professional prescribes. Proper management of diabetes can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the risk of long-term health problems.
Types of Diabetes and Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
There are two main types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that results in the body’s inability to produce insulin, while type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not use insulin effectively. It is important to note that proper management for each type of diabetes may differ, so it is best to consult your healthcare provider about which approach would be most suitable for you.
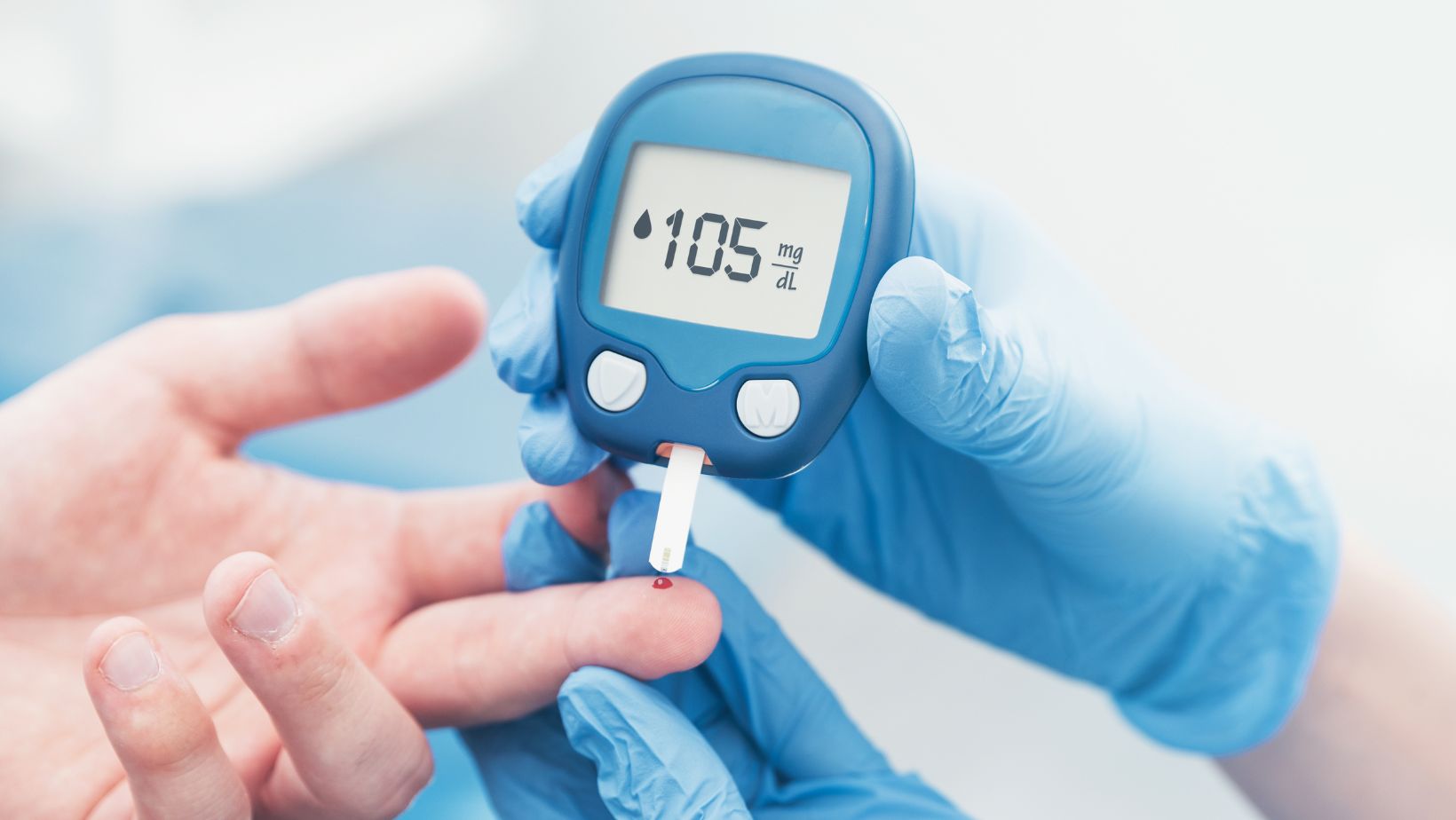
Blood glucose levels are an essential measure of diabetes management and can be tested using a home glucose meter to detect the amount of sugar in your blood. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes strive to keep their blood glucose levels between 80-130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL two hours after eating. If your levels are consistently higher than this, you must speak with your doctor about how to better manage them. Check out ozempicsingapore.com for more information.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels and Keeping Records
Regular monitoring of our blood glucose levels is essential to managing diabetes. It will help you better understand how lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, affect your blood sugar and give you an idea of when medication may need to be adjusted or added.
Keeping a detailed record of your blood sugar readings over time can be very helpful in tracking your progress and understanding which strategies are working to keep your levels in check. Your healthcare provider can use these records to help make decisions about optimal diabetes management, so it is essential to include them with any visits.
Differentiating Between Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Recognizing the difference between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia is essential, as both conditions can dramatically affect diabetes management. Hypoglycemia occurs when blood glucose levels are too low, while hyperglycemia happens when they are too high. Being familiar with both states and knowing how to respond in an emergency is vital.
Hypoglycemia usually occurs when someone with diabetes has taken too much insulin or has not eaten enough carbohydrates. The symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, dizziness, confusion, and sweating. Eating or drinking sugar-containing sugar such as fruit juice, candy, or glucose tablets is essential to respond to this condition.

Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is typically caused by insufficient physical activity or meal skipping. The symptoms of hyperglycemia include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. It is essential to take insulin if prescribed or drink plenty of water and rest until the symptoms subside to respond to this condition.
Dietary Adjustments to Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Making dietary changes can be a great way to manage blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Eating foods low in simple carbohydrates, such as white bread and pasta, and high in fiber, such as fruits and vegetables, can help maintain balanced blood sugar levels. Monitoring portion sizes and limiting sugary drinks or snacks may also help with diabetes management.
Consulting with a dietitian is beneficial in creating an individualized meal plan that fits your lifestyle and dietary needs. They can provide helpful guidance on making healthy food choices and portion sizes and teach you about carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and other beneficial nutrients for managing diabetes.