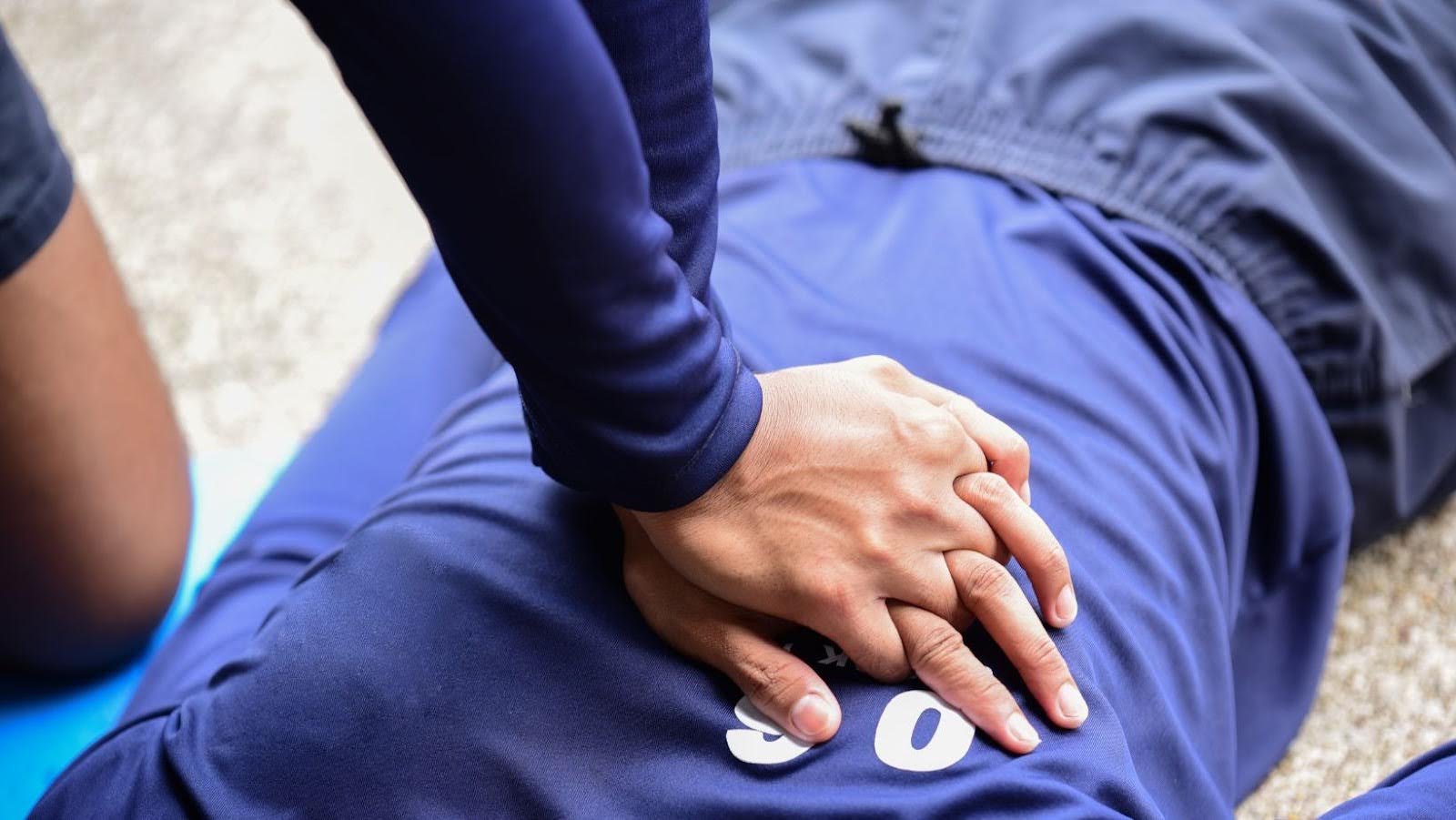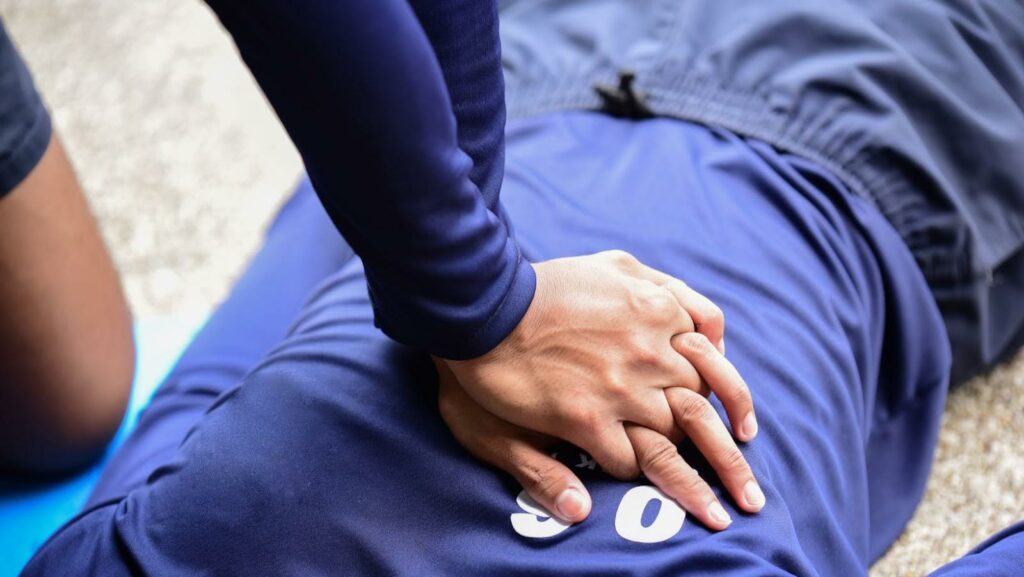
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR, is a life-saving technique used during emergencies to revive a person whose heartbeat or breathing has stopped. If performed accurately, CPR can improve a person’s chances of survival. This intervention is critical, especially during cardiac arrest. A primary component of CPR is maintaining the correct rate of CPR compressions.
Let us understand the advised rate at which CPR should be conducted, why it is crucial, and the guidelines for leveraging this procedure to save lives.
Importance of Maintaining the Correct Rate of CPR
CPR plays an essential role in maintaining the flow of oxygenated blood to vital organs, particularly the brain and heart. The rate at which chest compressions are administered directly impacts the effectiveness of blood flow and oxygen delivery. CPR trainers emphasize the importance of adhering to the proper compression rate to maximize the chances of survival in cardiac emergencies.
CPR can delay tissue death and extend the time available for a successful resuscitation without causing permanent damage to the body. This highlights the importance of providing effective and timely CPR training to improve the chances of a positive outcome during emergencies.
Understanding the Rate of CPR
The recommended rate of CPR for performing is 100 to 120 chest compressions per minute. This standardized guideline is established to optimize blood flow and oxygen delivery to vital organs during cardiac arrest. This rate balances the need for adequate circulation, minimizing rescuer fatigue and preventing incomplete chest recoil, which can occur at higher rates.
When you can deliver CPR swiftly and effectively, it benefits the patient and improves their chances of survival by the time advanced medical help arrives.
Performing CPR: Techniques and Considerations
To perform CPR effectively and at the recommended rate, you should follow specific techniques and considerations such as:
1. Hand Placement:
You need to place the heel of one hand on the center of the victim’s chest, with the other hand on top, interlocking fingers. You can then deliver compressions with the required force.
2. Compression Depth:
For adults, compress the chest at least one-third deep. The chest depth should be about one-third of that of children and infants.
3. Compression Quality:
Ensure that a complete chest recoil follows each compression. This will allow the heart to refill with blood between compressions, which is necessary for maintaining circulation.
4. Minimize Interruptions:
Minimize interruptions during chest compressions by aiming to keep them under 10 seconds whenever feasible. By limiting interruptions to chest compressions, we optimize the rate of CPR, increasing the likelihood of a positive outcome for the patient.
5. Use of Metronomes:
Metronomes, mobile apps, or other timing devices can provide auditory cues to maintain the correct CPR rate. These tools ensure compressions stay within the recommended rate, improving overall CPR quality.
Key Considerations for Effective CPR
Delivering timely CPR is crucial as it helps maintain blood flow and oxygen delivery to important organs, increasing the chances of survival in cardiac arrest situations. Delivering CPR late can have severe consequences, potentially resulting in fatalities or even brain damage due to oxygen deprivation. Swift and effective CPR, particularly when administered by trained individuals, significantly enhances the recovery of individuals experiencing sudden cardiac events.
Here are key considerations for ensuring timely and accurate CPR delivery:
1. Training and Awareness:
Proper training and regular practice are crucial to perform CPR. Organizations offer CPR certification courses that can help you learn the techniques correctly. Public awareness campaigns and training programs also help motivate people to learn CPR, creating a community prepared to respond to emergencies.
2. Challenges:
While maintaining the recommended CPR compression rate is crucial, rescuers may encounter difficulties such as anxiety and exhaustion. Physical exhaustion is a significant concern during CPR, as the demands of compressions at the prescribed rate and depth can rapidly tire even those in good physical condition.
Therefore, rotating every two minutes is advised to sustain effective compressions. Anxiety is another challenge, which can result in deviations from the correct compression rate and depth during CPR. These programs teach techniques to remain calm and focused, such as vocal counting or repeating rhythmic phrases, ensuring the required rate is maintained.
3. Ongoing Education and Refresher Courses:
CPR techniques and guidelines may evolve, making ongoing education and participation in refresher courses essential. Staying updated on the latest advancements in CPR ensures that you maintain proficiency. It also means you can respond effectively to cardiac arrest incidents.
Conclusion
Maintaining the correct rate of CPR and knowing the proper techniques to administer during medical emergencies can enhance the overall effectiveness of delivering CPR. Continuous training, public awareness, and learning aids are excellent tools to help you retain your knowledge of performing CPR. As a healthcare provider, you must continue to deliver CPR at the correct rate, as it can considerably improve patient outcomes. Learning how to perform the proper techniques will also allow you to administer CPR in a calm and collected manner.