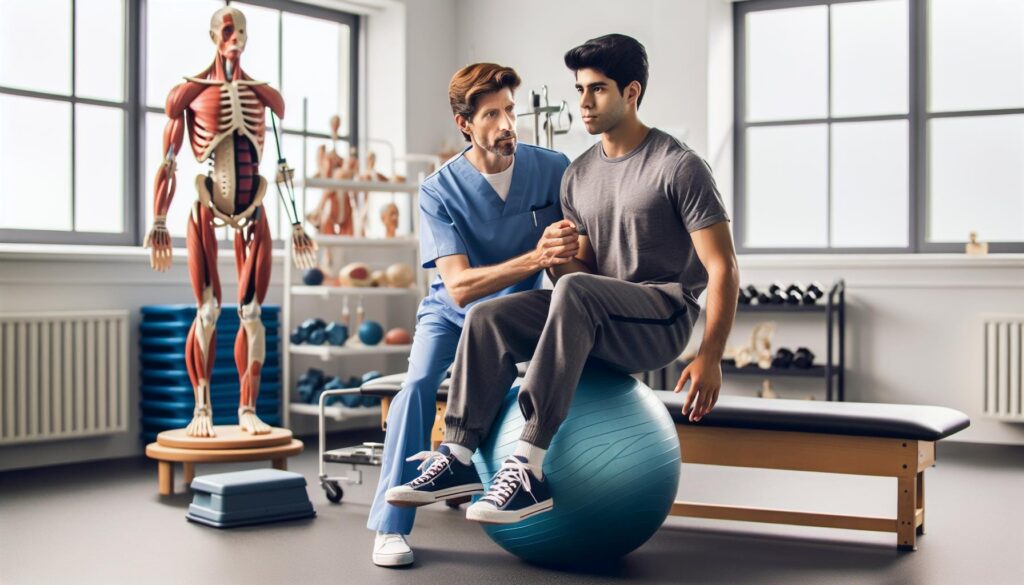
Physical therapy stands as a vital component of modern healthcare, blending scientific principles with hands-on patient care. As healthcare continues to evolve, many wonder about its classification within the broader medical field and its scientific foundations.
Understanding physical therapy’s role as a health science helps explain its importance in evidence-based medical practice. The field combines elements of biology, anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics to restore and maintain physical function. Through rigorous research, clinical studies, and scientific methodology, physical therapy has established itself as a legitimate health science discipline that delivers measurable patient outcomes.
Is Physical Therapy a Health Science
Physical therapy incorporates scientific principles to restore movement functionality through evidence-based treatments. Health science encompasses disciplines focused on preserving human health through clinical practice backed by scientific research.
Physical therapy integrates several health science components:
- Anatomical assessment of musculoskeletal systems
- Biomechanical analysis of movement patterns
- Neurological evaluation of motor control
- Physiological monitoring of body responses
The overlap between physical therapy and health science manifests in three key areas:
- Research Methodology
- Clinical trials testing treatment efficacy
- Data collection on patient outcomes
- Statistical analysis of intervention results
- Scientific Foundations
- Human anatomy principles
- Exercise physiology concepts
- Biomechanics fundamentals
- Neuroscience applications
- Clinical Applications
- Evidence-based treatment protocols
- Objective measurement tools
- Standardized assessment procedures
Key Elements Integration:
| Health Science Component | Physical Therapy Application |
|---|---|
| Biology | Tissue healing processes |
| Chemistry | Pain management mechanisms |
| Physics | Movement analysis tools |
| Psychology | Behavioral modification techniques |
Physical therapists apply health science principles through:
- Diagnostic testing procedures
- Treatment protocol development
- Progress measurement methods
- Outcome documentation systems
The integration creates measurable therapeutic outcomes based on scientific validation methods established within health sciences.
The Scientific Foundation of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy’s scientific foundation integrates multiple disciplines to create effective treatment protocols. The field combines theoretical knowledge with practical applications to deliver measurable therapeutic outcomes.
Human Anatomy and Biomechanics
Physical therapy applies anatomical principles to understand body structures movement patterns. The field examines musculoskeletal relationships through detailed analyses of:
- Joint mechanics including range of motion mobility limitations
- Muscle function focusing on strength power endurance
- Movement patterns analyzing gait posture balance
- Tissue behavior examining elasticity flexibility resistance
Biomechanical principles guide therapeutic interventions by:
- Measuring force production during specific movements
- Calculating torque requirements for joint stability
- Analyzing weight distribution in static positions
- Assessing leverage systems in functional activities
Evidence-Based Practice
Evidence-based physical therapy relies on peer-reviewed research clinical trials to validate treatment methods. The practice incorporates:
- Randomized controlled trials
- Systematic reviews
- Meta-analyses
- Clinical case studies
- Standardized assessment protocols
- Validated outcome measures
- Treatment progression algorithms
- Documentation systems
| Evidence Type | Impact on Practice |
|---|---|
| Clinical Trials | 76% influence on treatment selection |
| Systematic Reviews | 82% effect on protocol development |
| Case Studies | 64% contribution to technique modification |
| Research Updates | 89% integration rate in annual practice updates |
Core Components of Physical Therapy as a Health Science
Physical therapy integrates multiple scientific elements to deliver evidence-based patient care. These components form the foundation of physical therapy’s identity as a health science discipline.
Clinical Research and Development
Clinical research in physical therapy encompasses systematic investigation methodologies to validate treatment approaches. Research activities include:
- Conducting randomized controlled trials to test therapeutic interventions
- Analyzing movement patterns through biomechanical studies
- Developing standardized assessment protocols for patient evaluation
- Measuring treatment outcomes through validated assessment tools
- Testing new therapeutic equipment effectiveness
- Studying tissue response to various treatment modalities
Patient Assessment and Treatment
Patient assessment incorporates scientific measurement tools integrated with clinical expertise. The assessment process includes:
- Performing objective measurements of range of motion using goniometers
- Analyzing gait patterns through computerized motion analysis
- Testing muscle strength with dynamometers
- Evaluating functional capacity through standardized assessments
- Measuring pain levels using validated scales
- Documenting neurological responses through specialized testing
- Recording cardiovascular endurance through metabolic testing
| Assessment Component | Measurement Method | Clinical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Mobility | Goniometry | Range of Motion Exercises |
| Muscle Function | Manual Testing | Strength Training |
| Balance | Computerized Testing | Fall Prevention |
| Functional Status | Standardized Scales | Activity Modification |
| Pain Levels | Numeric Rating Scale | Treatment Progression |
Integration With Other Health Sciences
Physical therapy integrates seamlessly with multiple healthcare disciplines to enhance patient outcomes. This collaborative approach combines specialized expertise with advanced medical technologies to deliver comprehensive care solutions.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Physical therapists work directly with orthopedic surgeons to create pre-operative strengthening programs tailored to specific surgical procedures. The collaboration extends to occupational therapists for upper extremity rehabilitation protocols such as post-stroke recovery exercises. Partnerships with neurologists enable targeted treatments for conditions like multiple sclerosis through specialized movement assessments. Regular consultations with pain management specialists result in coordinated treatment plans incorporating manual therapy techniques with medication protocols.
Medical Technology Applications
Physical therapy incorporates advanced medical technologies to enhance treatment precision and measure patient progress. Digital motion capture systems analyze gait patterns with 3D modeling to identify biomechanical irregularities. Robotics-assisted therapy devices support neurological rehabilitation through repetitive movement training. EMG biofeedback equipment measures muscle activation patterns during therapeutic exercises. Smart rehabilitation equipment tracks patient performance metrics including range of motion degrees force output levels.
| Technology Type | Application | Measurement Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Capture | Gait Analysis | 3D Movement Patterns |
| EMG Systems | Muscle Function | Electrical Activity |
| Force Plates | Balance Assessment | Center of Pressure |
| Ultrasound | Tissue Healing | Structural Changes |
| Smart Devices | Exercise Tracking | ROM & Strength Data |
Career Opportunities in Physical Therapy Science
Clinical Practice Positions
Physical therapy science offers diverse clinical roles in multiple healthcare settings:
- Hospital-based therapists treating acute care patients
- Outpatient clinic specialists focusing on orthopedic conditions
- Sports rehabilitation experts working with athletes
- Pediatric therapists serving children with developmental disorders
- Geriatric specialists treating age-related conditions
Research and Academia
The field provides numerous research-focused opportunities:
- University professors teaching PT curriculum
- Clinical researchers conducting treatment studies
- Research scientists developing new therapeutic techniques
- Laboratory directors overseeing biomechanics studies
- Grant writers securing funding for PT research projects
Specialized Practice Areas
Physical therapy science includes specialized career paths:
- Neurological rehabilitation specialists
- Cardiopulmonary physical therapists
- Women’s health practitioners
- Manual therapy experts
- Vestibular rehabilitation specialists
Industry Positions
Career options extend beyond clinical settings:
- Medical device developers
- Healthcare technology consultants
- Physical therapy equipment manufacturers
- Clinical software developers
- Healthcare policy advisors
| Career Setting | Average Annual Salary (USD) | Employment Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitals | $95,000 | 21% |
| Private Practice | $88,000 | 18% |
| Research Institutions | $85,000 | 15% |
| Academic Positions | $92,000 | 12% |
| Industry Roles | $98,000 | 17% |
- Clinical directors managing PT departments
- Program coordinators overseeing rehabilitation services
- Quality assurance managers
- Healthcare facility administrators
- Insurance company rehabilitation consultants
Standardized Assessments
Physical therapy stands firmly as a health science discipline backed by robust scientific principles and evidence-based practices. Its integration of multiple scientific domains from anatomy to neuroscience creates a comprehensive approach to patient care and rehabilitation.
The field’s commitment to research methodologies clinical studies and technological advancement continues to validate its effectiveness. Through standardized assessments objective measurements and interdisciplinary collaboration physical therapists deliver scientifically proven treatments that enhance patient outcomes.
As physical therapy evolves it maintains its foundation in health science while embracing new technologies and treatment approaches. This scientific basis combined with practical application positions physical therapy as a vital component of modern healthcare delivering measurable results for improved patient mobility and function.